M. Korman, W. Mulzer, A. van Renssen, M. Roeloffzen, P. Seiferth,
Y. Stein, B. Vogtenhuber, and M. Willert
A routing scheme
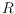
in a network
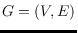
is an algorithm that allows to
send messages from one node to another in the network. We are first allowed a
preprocessing phase in which we assign a unique
label to each node
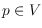
and a
routing table with additional information. After this
preprocessing, the routing algorithm itself must be local (i.e., we can only
use the information from the label of the target and the routing table of the
node that we are currently at). We present a routing scheme for routing in
simple polygons: for any
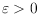
the routing scheme provides a
stretch of
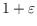
, labels have
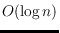
bits, the corresponding
routing tables are of size
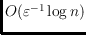
, and the preprocessing
time is
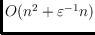
. This improves the best known strategies
for general graphs by Roditty and Tov (Distributed Computing 2016).