O. Aichholzer, G. Araujo-Pardo, N. García-Colín, T. Hackl,
D. Lara, C. Rubio-Montiel, and J. Urrutia
The pseudoachromatic index of a graph is the maximum number of colors that can
be assigned to its edges, such that each pair of different colors is incident
to a common vertex. If for each vertex its incident edges have different
color, then this maximum is known as achromatic index. Both indices have been
widely studied. A geometric graph is a graph drawn in the plane such that its
vertices are points in general position, and its edges are straight-line
segments. In this paper we extend the notion of pseudoachromatic and
achromatic indices for geometric graphs, and present results for complete
geometric graphs. In particular, we show that for n points in convex position
the achromatic index and the pseudoachromatic index of the complete geometric
graph are
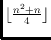
.